Cytokines and growth factors that are produced by or have an effect on adipocytes and related peptide neuro-transmitters are central players in hunger vs. satiety balance and in eating behavior (1). Recent evidence shows that adipokines, and more generally mediators or indicators of inflammation (2), play roles in the development of insulin resistance (3), diabetes (4) and many other concomittant health problems associated with obesity, including hypertension, dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis (5).
Adipokine monitoring during Hunger and Satiety balance
RhoA/ROCK and F-actin modeling involved in Insulin secretion
This is the conclusion of Liu X. et al. who demonstrated, in a mouse model, that RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway modulates insulin secretion of 3D cultured islet pancreatic ß-cells. This modulation is made through the regulation of Connexin 36.
Cell-permeable C3 transferase (C3T; Cytoskeleton Inc.) and the small molecule Y-27632 ROCK inhibitor (Stemgent-Asterand) were used in these studies.
External links regarding RhoA/ROCK in insulin secretion of pancreatic ß-cells
- Liu X. et al. “Involvement of RhoA/ROCK in insulin secretion of pancreatic ß-cells in 3D
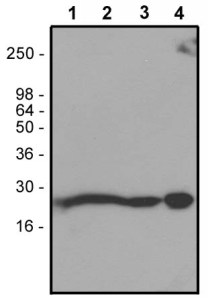
Western blot detection of RhoA (cat. nr ARH03) in cell extracts (50 µg each) of rat NRK cells (lane 1), human HeLa cells (lane 2), bovine brain extract (lane 3), and human platelet cell extract (lane 4).
culture” (2014) Cell Tissue Res. DOI: 10.1007/s00441-014-1961-2
- Cell permeable C3 transferase (cat. nr CT04), inhibits cellular Rho within 2-4h
- Selective Rho Kinase (ROCK) inhibitors and anti Human RhoA antibody (a Mouse monoclonal that only recognizes RhoA, not RhoB, RhoC, Rac1, Rac2, Rac3, Cdc42 or H-Ras).
I hope you will enjoy this new publication. Don’t hesitate to leave your comments or remarks regarding the use of bioactive small molecules in signal transduction studies.
Obesity, Diabetes, Metabolic syndrome new research tools
Insulin and Glucagon are involved in glucose homeostasis in addition to other factors secreted by the adipose tissue (adipokines). Insulin and Glucagon are produced by the endocrine pancreas. While Glucagon is released by alpha-cells of the islets of Langerhans to raise glycemia when blood glucose levels fall too low, Insulin has the opposite effect. Insulin is produced by beta-cells of the islets of Langerhans. It allows glucose to be taken up from the bloodstream when blood glucose levels are high and to be used by insulin-dependent tissues (liver, skeletal muscles, fat tissue…).
Let’s take a look at a selection of immuno-assays and primary cells for analysing these two hormones and the recentlly launched primary Human Islet cells.




